Key Takeaways:
- Electrolysis can create hydrogen, a known green fuel, but the process still relies heavily on fossil-fuel-created electricity.
- Electrolysis has a variety of uses across numerous industries, including extracting valuable metals and chemicals.
- Electrolysis has a bright future in sustainability, but it requires advancements in sustainable energy to push it further.
You might have heard of electrolysis in relation to hair removal, but this electrified process goes well beyond the beauty industry. Electrolysis is an electrochemical process that breaks down a compound using an electric current. It does so by using an energy source to drive chemical reactions and produce the desired outcome.
As you’ll soon learn, electrolysis reactions form the basis of modern industry. Learn more about electrolysis, how it differs from other electrochemical processes, its common applications, and how it’s a promising option for a green energy future.
What Is Electrolysis and How Does It Differ From Other Electrochemical Processes?
Electrolysis is an electrochemical process crucial in various industries and scientific applications. It involves breaking down a compound into constituent elements or ions using an electric current. The flow of electrons from the anode (the positively charged electrode) to the cathode (the negatively charged electrode) drives the process, leading to chemical reactions that result in the desired products.
One key difference between electrolysis and other electrochemical processes, such as galvanic cells, is their energy requirement. Galvanic cells produce electricity through spontaneous redox reactions, whereas electrolysis requires an external energy source to drive its reactions. The electrolytic cell requires this external energy input to overcome the activation energy barrier and execute the desired chemical transformations.
Electrolysis offers unique versatility in its applications. It can help obtain a desired substance at the electrode through processes like electroplating and can decompose compounds into their constituent elements through electrolytic decomposition. This versatility makes electrolysis a valuable tool across numerous industries, such as metal refining, wastewater treatment, and the production of chemicals and materials.
Which Substances Can Undergo Electrolysis? What Are the Key Requirements for the Process?
Various substances can undergo electrolysis, including molten salts and aqueous solutions. The key requirement for electrolysis is that the electrolyzed substance must be an electrolyte (an electrically conductive medium). It requires this because the electric current must flow through the electrolyte to facilitate the chemical reactions.
The presence of an electrolyte isn’t the only requirement for electrolysis. This process also requires two electrodes known as an anode and a cathode, which are typically made from conductive materials, such as metal or graphite, and connect to the power source.
The anode receives a positive charge, while the cathode receives a negative charge. This results in the positive ions being attracted to the cathode, where they receive electrons and are reduced. On the other side, the negative ions are attracted to the anode, where they lose electrons and oxidize.
What Are the Applications of Electrolysis in Industries?
Electrolysis has wide-reaching applications in numerous industries, but a common application is in metal extraction. Electrolysis can help extract valuable metals, such as aluminum and copper, from their ores. This process reduces the metal ions at the cathode, resulting in an easily collected pure metal deposit.
Water treatment is another electrolysis application. Electrolysis can remove impurities in the water, including heavy metals and bacteria. During the electrolysis of water, the impurities are attracted to the electrodes or undergo chemical reactions that transform them into less harmful substances.
Furthermore, electrolysis plays a crucial role in chlorine and sodium hydroxide production. This process, known as chlor-alkali electrolysis, involves the electrolysis of a sodium chloride solution. This electrolysis works by oxidizing the chlorine ions at the anode to produce chlorine gas while reducing water at the cathode to produce hydrogen gas and hydroxide ions, which then react to form sodium hydroxide.
Electrolysis also plays a role in healthcare as an alternative hair removal process to waxing, shaving, or laser hair removal called electrology. In this process, the healthcare professional inserts a fine needle into the hair follicle and applies a small electrical current to destroy the root of the hair.
Electrolysis is a permanent hair removal solution for people seeking long-term results against future hair growth. The precision and effectiveness of electrolysis make it a popular choice for those seeking permanent elimination of unwanted hair.
Enter your ZIP Code and compare electricity rates
What Role Does Voltage and Current Play in Driving Electrolysis Reactions?
Voltage and current are critical in driving electrolysis reactions. The voltage heading through the electrodes determines the electric field’s strength and controls ion movement within the electrolyte. The greater the voltage, the stronger the electric field, thereby increasing the electrolysis reaction rate. But keep in mind that too much voltage can cause undesired side reactions or damage the electrodes.
The current flowing through the electrolyte determines the rate at which the reactions take place. Higher currents increase the electrolysis rate, leading to higher energy consumption and can cause the electrolyte to heat up. This is why balancing voltage, current, and reaction rate is critical to efficient electrolysis.
What Are the Common Electrolysis Reactions in Producing Metals and Other Valuable Substances?
Electrolysis is often used to produce metals and other valuable substances. One example is aluminum production, which involves the electrolysis of molten aluminum oxide. In the aluminum-producing process, aluminum ions are reduced at the cathode, forming molten aluminum. At this point, the molten aluminum is collected for use in various goods.
As we discussed earlier, electrolysis of a sodium chloride solution helps produce valuable chlorine gas and sodium hydroxide. The chlorine ions oxidize at the anode to form chlorine gas, while hydrogen gas and hydroxide ions form through water molecule reduction at the the cathode. The hydrogen gas, water, and hydroxide ions then react to form sodium hydroxide.
This process has important applications in the chemical industry. For example, chlorine gas helps in the manufacturing of paper, cloth, pesticides, rubbers, and more. Sodium hydroxide, on the other hand, goes into the manufacturing of soaps, rayon, dyes, petroleum products, and more.
What Are Environmental Considerations and Challenges With Industrial Electrolysis Processes?
Industrial electrolysis processes can impact the environment positively and negatively.
On the positive side, electrolysis can help support clean energy. It is one process for creating hydrogen gas, which can be used as a fuel or feedstock for synthesizing various chemicals.
However, industrial electrolysis processes have some negative environmental effects. One significant issue is its energy consumption. Electrolysis needs a lot of energy to work properly, and this energy isn’t always from renewable sources like hydroelectric power or solar panels. By increasing the focus on switching to renewable energy, we can help minimize the negative environmental impact of electrolysis processes.
Another negative for electrolysis is its waste production. Using electrolysis results in hazardous waste that we must find a way to dispose of properly.
Finally, extracting the raw materials needed to perform electrolysis can be harmful to the environment. For example, mining for aluminum could result in soil erosion and deforestation.
How Is Electrolysis Used in Technologies Like Electrolytic Cells and Batteries?
Electrolysis is an essential process in electrolytic cells and batteries. Electrolytic cells use electrolysis as a driver of non-spontaneous chemical reactions, including producing chlorine gas or the electroplating of metals. A wide range of industries uses these cells, including chemical production and electricity generation.
Batteries use electrolysis but not in the way you might expect. When you recharge a battery, it relies on electrolysis to do so. The battery relies on an external power source (the charger) to drive the battery’s cell reactions backward, restoring its voltage.
What Advancements Are There in Electrolysis for Sustainable and Efficient Applications?
Electrolysis has many innovations aimed at making the process more sustainable and efficient. For example, ongoing research is exploring the use of catalysts and nanostructured materials to improve electrolytic cell performance.
As discussed, electrolysis requires a large amount of energy, which can negatively affect natural environments. To help counter this, integrating renewable energy sources with electrolysis is the next big step in making it more sustainable. By substituting renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, in place of grid-drawn energy, we can greatly reduce the negative environmental impact of electrolysis. Many refer to this approach as “green electrolysis,” and it can potentially contribute to a more sustainable energy system.
How Is Electrolysis Applied in Hydrogen Production for Clean Energy and Fuel Cell Technologies?
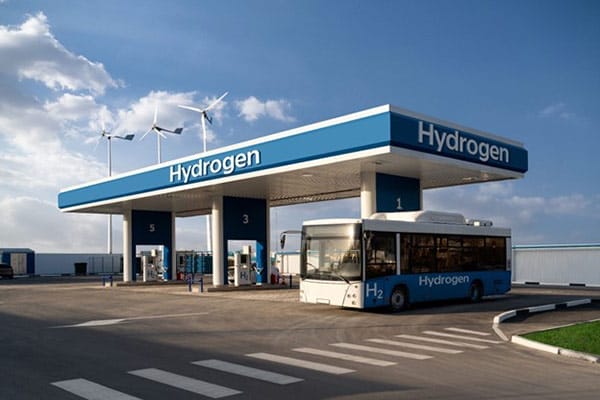
A very promising application of electrolysis is in producing hydrogen that’ll act as clean energy for fuel cell technologies. Electrolysis can split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen gases through a process called water electrolysis. The hydrogen gas that this process produces works as a clean, renewable energy source in any process that requires hydrogen as a fuel.
Electrolysis-produced hydrogen is safe to use directly in fuel cells to generate electricity. How do these fuel cells work? They combine hydrogen molecules with oxygen molecules, which creates a small amount of electrical energy that’s used as an energy source. And because the electricity only comes from the combination of hydrogen and oxygen molecules, the only emission byproduct is water.
Fuel cells are an especially attractive technology for powering vehicles and other applications that require clean and efficient energy sources. This technology is still in its infancy, with only a few notable fuel cell vehicles making it to production, including the Toyota Mirai, Hyundai Nexo, and Honda Clarity.
Furthermore, electrolysis can be integrated with renewable energy sources to produce hydrogen, providing a sustainable way to store and utilize excess energy.
Electrolysis Is a Powerful Process that Can Reduce Reliance on Fossil Fuels
Electrolysis is a versatile electrochemical process crucial in many industries and technologies. While you might have known about it as a hair removal method, there’s much more to it.
Whether it’s metal extraction or water treatment, electrolysis has a wide range of uses. Its most beneficial application for the environment is the production of hydrogen gas that can fuel eco-friendly fuel cells.
However, the technology is still developing to fine-tune its “green” credentials. Research and advancements aim to make electrolysis more sustainable and efficient by integrating renewable energy sources. This can help pave the way for a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Brought to you by energysavings.com
All images licensed from Adobe Stock.